POOPOLOGY: What You Can Learn From “Reading the Paper”
By Louisa Jaskulski, RVT
Photographs by Dr. Chris Sanders, DVM, Wildwood Veterinary Hospital
Birds are “masters of disguise” when it comes to hiding early signs of illness. Therefore, exterior indicators of health status are very helpful and important. Bird droppings are one of those critical exterior indicators, in conjunction with clinical signs such as fluffed feathers, energy level, loss of appetite, weight loss, and so forth.
Among the many ways birds differ from mammals is the body’s product exit design. Mammals have separate tubes and exit openings for the 3 major exiting products - babies/sperm (reproductive organs), urine (kidneys), and feces (digestive system). Mammals have a bladder which stores urine after it leaves the kidneys - birds do not. Although birds also have separate tubes from the reproductive organs, kidneys, and digestive tract, all of them meet in a compartment called the cloaca. Functionally it means that the waste products produced by the kidneys and the waste material generated by the digestive system all meet in this compartment, and leave together at the same time out of the cloaca. This is what we call the bird’s droppings, or “poop”. (Eggs and sperm also depart out of the cloaca, but not in conjunction with the droppings.)
Droppings consist of three parts. There is fecal matter from the digestive system, generally located in the center of the dropping. The feces are surrounded by white chalky material called urates, which are in turn surrounded by clear liquid urine. Urates and urine are both produced by the kidneys. The urates result from protein break down, and are unique to birds and reptiles. Sometimes there are only feces, urates or urine, but usually droppings contain all three.
Droppings can be an important window, if not to the soul, certainly into the health status of your bird. It is essential to know what normal healthy droppings look like for your bird, so you can tell if there are changes signaling illness.
 Normal droppings on newspaper Normal droppings on newspaper |
It is best to use only paper on the bottom, and to change it daily, as this allows you to easily see the overall appearance, consistency, volume, color and frequency of the droppings on a daily basis. Some abnormalities merit a visit to your avian veterinarian as soon as possible. If the droppings have changed without any change in diet or routine, then something could be wrong. |
1. OVERALL APPEARANCE AND CONSISTENCY
Birds have a rapid gastrointestinal transit time - food moves through them in a matter of hours. Therefore, you can tell whether or not your bird is eating by looking for droppings that contain fecal matter (this assumes you have fresh paper on the bottom of the cage which is changed at least once a day, of course - you cannot tell any of this if the bottom is covered in old droppings!). If you see fecal matter in the droppings, your bird is eating. |
 Filthy cage bottom, with pellet substrate Filthy cage bottom, with pellet substrate |
*** See your avian veterinarian if – you see only urates and urine, with no feces. If this persists for more than a few hours, the bird is not eating, and that often means a serious problem.
Bird of species that come from arid regions, such as budgies and zebra finches, will tend to have smaller, drier droppings. Birds of species from tropical regions that eat foods with higher water content (vegetables and fruit) will have larger droppings. The fecal material should be formed, generally tubular, internally uniform, and are often coiled. Nectar eaters, such as Lories, have very liquid droppings, so the fecal tubes are more loosely formed.
*** See your avian veterinarian if - the feces contain partially digested food, or are smelly, slimy, or foamy. Partially digested food can be due to viral disease. Slimy droppings can be caused by an overgrowth of yeast. Foamy or bubbly droppings can be caused by bacterial infection such Clostridium, a type of nasty bacteria.
 Fecal stained feathers of a Fecal stained feathers of a chicken's hind end |
*** See your avian veterinarian if - the feces themselves are watery and unformed, and look like pudding or spattered pea soup, as this may mean diarrhea. Diarrhea is not the same as wet droppings due to increased urine. Causes of transient diarrhea which should resolve quickly when the cause is removed include stress, introducing a new food too quickly, eating spoiled or rancid food, or exposure to irritating inhalants. More serious causes include bacterial or fungal infection, intestinal parasites, toxins, foreign objects in the gastrointestinal tract, or antibiotics. With diarrhea, feces can stick to the vent, so the vent area and/or feathers under the vent are dirty. |
If you suspect diarrhea, contact your avian veterinarian immediately, because it can cause birds to become dehydrated and die very quickly! The urates that surround the feces are a thick liquid, and should be a chalky white or cream color, although they may be colored by pigments in colored foods. The liquid urine is normally clear, and can vary in amount depending on species and diet. |
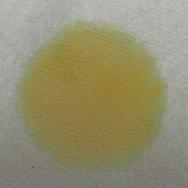 Colored urine after eating a colored pellet Colored urine after eating a colored pellet |
2. VOLUME
Volume of the Formed Fecal Portion of the Dropping
Less feces in the droppings than usual can result from decreased food intake, food deprivation or food going through too fast due to a gastrointestinal problem. Small dry feces can be due to dehydration or organ disease.
*** See your avian veterinarian if – the fecal content remains low even if your bird has adequate food available.
Increased fecal volume or bulk is sometimes normal – in the first droppings in the morning, from hormonal or egg laying females who hold their poop while on the nest and then expel a large dropping when they leave the nest, or from eating a lot of vegetables, fruit, or moist food.
*** See your avian veterinarian if - the fecal portion of the dropping continues to be increased without those factors being present, as this can indicate food is not being absorbed due to any number of problems with the gastrointestinal tract (infection, diabetes, kidney or liver disease, parasites, cancer) that must be evaluated and treated by your avian veterinarian.
Volume of the Urate Portion of the Dropping
Increased volume of the urates can be caused by the type of diet, inadequate water intake, dehydration, or by kidney problems.
*** See your avian veterinarian if – the increased urates volume continues after ensuring your bird has enough water.
Volume of the Urine Portion of the Dropping
Normal urine volume varies by species, from being a small amount in seed-eating birds from arid regions, to large volume for nectar eaters and water birds. Increased urine output (which looks like an enlarged “halo” of thin liquid) results in a wet dropping. An increase over what is normal for that species may be significant. Transient increases may be due to eating larger amounts of moist fresh food such as apple or melon, drinking a lot of water during a bath, stress (travel, a new cage location, new people or pets in the home, etc), or being too hot . Urine output should return to normal about an hour after the stimulating condition is removed.
*** See your avian veterinarian if - droppings remain abnormally wet with increased urine output, as this can be due to kidney or liver disease, infection, diabetes, toxins, cancer, metabolic imbalances, or nutritional imbalances (too much salt, insufficient vitamin A or D, for example). Increased urine output (polyuria) may be accompanied by increased thirst/drinking (polydipsea), and/or a persistently wet cloacal area. Try to monitor if your bird is drinking more by watching how often he/she visits the water bowl and how many sips of water are consumed. These are serious, complex problems that should be evaluated by your avian veterinarian as soon as possible.
3. COLOR
 Pomegranate-stained feces and urine Pomegranate-stained feces and urine |
Color of the Fecal Portion of the Dropping The fecal portion will usually reflect the color of the food items being eaten. For example, birds eating primarily seed will usually have dark green feces; feces from eating uncolored pellets will usually be tan or brown; feces from eating colored pellets will be those colors; carrots and baked sweet potatoes result in orange feces; blueberries, cherries, pomegranate will result in dark red or purple feces. This is normal and not a problem - though many an owner who feared their bird was bleeding internally because of dark poops has been reassured to learn it was actually just the pigment in the blueberries!! |
*** See your avian veterinarian if - you see unusual colors in the feces. Some colors are of great concern and should be evaluated by your avian veterinarian immediately. Bright red blood indicates bleeding near the cloaca. Black tarry feces points to bleeding further up the gastrointestinal system such as the proventriculus (the glandular stomach) or the gizzard/ventriculus (the muscular grinding stomach). Such bleeding has many possible causes, including inadequate food intake, infection, cancer, toxins, or viral disease. Bright green or yellow feces can signify that the bird is not eating (anorexia), liver disease, or Chlamydia (a kind of bacteria) infection. |
 Tarry feces (on top), blood in urates, increased
urine - from kidney infection Tarry feces (on top), blood in urates, increased
urine - from kidney infection |
 Green undigested food and green urine - due to heavy metal toxicity Green undigested food and green urine - due to heavy metal toxicity |
Color of the Urates Portion of the Dropping The chalky urates are normally white, cream colored or slightly yellow. If the feces are colored by the color of food items, this color can leach out into the urates, and does not indicate a problem. It is normal to have some mild transient color changes throughout the day depending on what the bird is eating. |
*** See your avian veterinarian if – you see unusual colors in the urates. Some colors are of great concern and merit prompt veterinary attention. Bright green or yellow urates can indicate liver disease, Chlamydia infection, or anorexia (loss of appetite). Brown urates can be caused by lead poisoning. Red urates can result from heavy metal toxicity, internal bleeding or kidney problems. If a bird has bright green or yellow feces due to Chlamydia, this color can leach into the urates as |
 Yellow urine and urates - due to liver disease Yellow urine and urates - due to liver disease |
Color of the Urine Portion of the Dropping
*** See your avian veterinarian if – you see color changes in the urine. Urine is normally clear, so pay close attention to any color change. A greenish or yellowish tinge points to liver disease, whereas reddish brown urine is consistent with heavy metal poisoning.
4. FREQUENCY
*** See your avian veterinarian if – you see an increased number of droppings, indicating that your bird is defecating more often than usual. Depending on the actual appearance of the droppings, this could be due to diarrhea or many of the other issues discussed above.
*** See your avian veterinarian if - you see a decreased number of droppings, which can be due to a loss of appetite, a big worry for birds due to their high metabolic rate. Sometimes the decreased number of droppings is due to a blockage, so if you see a swollen abdomen, hunched over posture, or straining, this can constitute an emergency.
CONCLUSION
Abnormal droppings are not themselves an illness, but are instead an indicator of illness. Your avian veterinarian will work with you to determine the best diagnostic procedures to discover the underlying cause. It is always better to catch these problems sooner rather than later, and hopefully you will be better able to “read the paper” in your bird’s cage to make you a better bird health detective!

